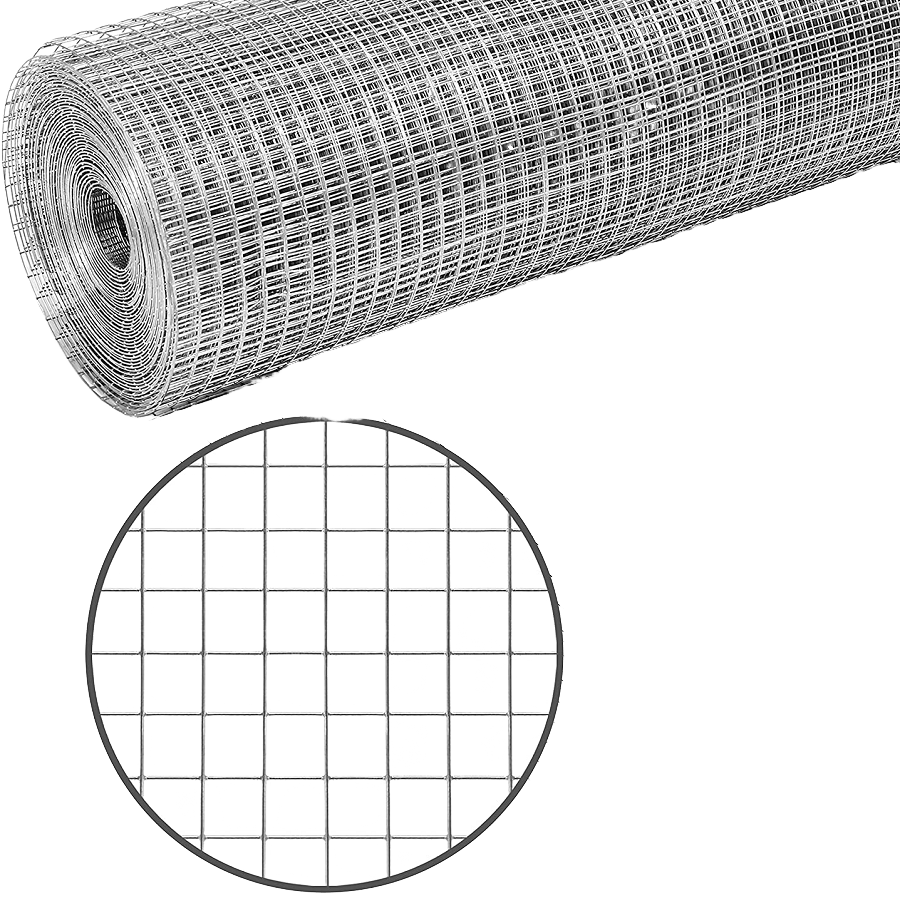
溶接金網の基本ガイド: 強さ, 多用途性, とアプリケーション
Welded wire mesh, 基礎的かつ汎用性の高い産業資材, is engineered by precisely welding together intersecting wires at their contact points. This process creates a grid of uniform strength and regularity, distinguishing it from woven alternatives. Primarily manufactured from low-carbon steel wire, ステンレス鋼, or galvanized wire, it can also be fabricated from materials like PVC-coated steel or aluminum for specific needs. The welding is typically performed using automated electric resistance welders, ensuring consistency and high-volume production.
Key Characteristics and Advantages
The popularity of welded wire mesh stems from a combination of structural and practical benefits:
High Strength and Rigidity: The welded junctions lock the wires in place, creating a rigid, non-flexing panel that can withstand significant loads and stress without deformation. This makes it ideal for structural applications.
Uniformity and Precision: The grid pattern is consistent, with precise aperture (opening) sizes and wire diameters. This predictability is crucial for sorting, スクリーニング, and architectural uses.
耐久性: Depending on the material, it offers excellent resistance to wear, impact, and environmental factors. Galvanized welded mesh (with a zinc coating) provides superior corrosion resistance for outdoor and industrial use.
Versatility in Design: It can be produced in a vast range of specifications: wire gauge (thickness), メッシュサイズ (aperture dimensions), panel sizes, and roll lengths. This allows for customization to exact project requirements.
Ease of Installation: The panels are flat and can be quickly cut, shaped, and installed using simple tools—tying, clipping, or even welding them into place.
Common Types and Materials
Electro-Galvanized Welded Mesh: Features a thin zinc coating applied after welding. Suitable for indoor use or mild environments where rust prevention is a minor concern.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Welded Mesh: Immersed in molten zinc after welding, providing a thick, durable coating that offers long-term corrosion protection for fencing, cages, and agricultural use.
Stainless Steel Welded Mesh: Made from 304 または 316 ステンレス鋼, this type delivers exceptional corrosion resistance, hygiene, and strength. It is essential for food processing, chemical industries, marine environments, and architectural accents.
PVC-Coated Welded Mesh: A steel wire mesh coated with a layer of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), usually in green or black. The coating adds an extra layer of protection against corrosion and provides a more aesthetically pleasing finish for fencing, partitions, and animal enclosures.
Primary Applications Across Industries
Welded wire mesh is ubiquitous in modern infrastructure and manufacturing:
- 工事 & コンクリート補強:
溶接ワイヤーファブリック (WWF) or Mesh Sheets: Laid within concrete slabs (床, 舗装, foundations) to control cracking, increase tensile strength, and distribute loads evenly.
- Fencing, 安全, and Enclosures:
Perimeter fencing for industrial sites, schools, and residential properties.
Animal cages and pens in agriculture and zoos.
Security screens for windows and doors.
Machine guards and safety partitions in factories.
- Industrial and Storage Solutions:
Storage Racks and Shelving: Used as decking for pallet racks and shelving units.
Partitions and Cages: For secure storage, lockers, and material segregation.
Gabions: Large, modular cages filled with stone used for erosion control, retaining walls, and landscaping.
- Agricultural and Horticultural:
Tree Guards and Plant Supports: Protects saplings and supports climbing plants.
Poultry and Animal Cages: Including rabbit hutches and aviaries.
Compost Bins and Gardening Screens.
- Infrastructure and Civil Engineering:
Reinforcement in drainage systems and culverts.
Rockfall and slope stabilization nets.
Reinforcement for roads and pipelines.
- Other Specialized Uses:
Architectural Mesh: Used as decorative cladding, balustrades, and sunscreens for modern buildings.
Shopping Carts and Baskets.
Filters and Sieves in various processing industries (size and material dependent).
Selection Considerations
Choosing the right welded wire mesh involves evaluating several factors:
Material and Coating: Determine the required level of corrosion resistance based on the environment (indoor, outdoor, harsh chemical exposure).
Mesh Size (Aperture): The size of the openings, which affects visibility, 気流, material passage, and security level.
Wire Diameter (Gauge): Thicker wires provide greater strength and rigidity.
Panel Size and Format: Available in flat sheets or rolls, with custom dimensions often available.
結論
Welded wire mesh is an indispensable engineered product that combines simplicity of design with remarkable functional strength. Its adaptability across countless sectors—from reinforcing skyscrapers and highways to securing backyards and supporting agriculture—highlights its fundamental role in construction, industry, and daily life. Understanding its properties, types, and applications allows for the specification of the optimal mesh solution, ensuring performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness for any project.
 メイドインメッシュ
メイドインメッシュ